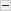
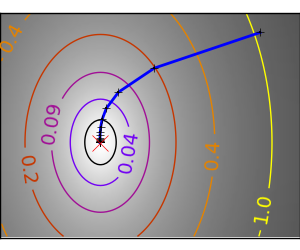
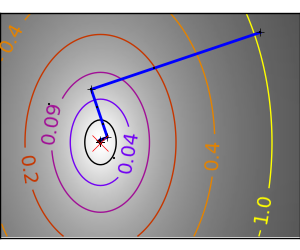
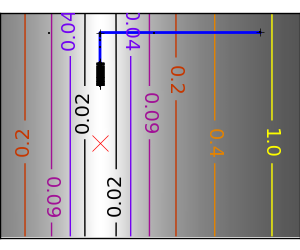
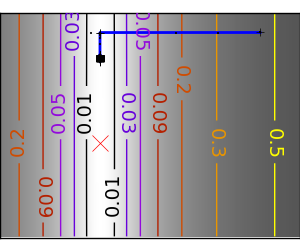
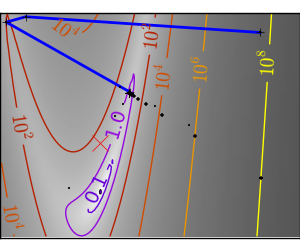
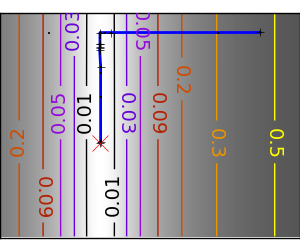
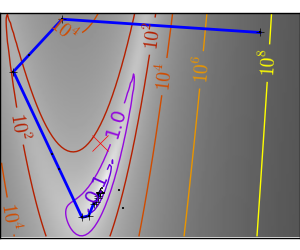
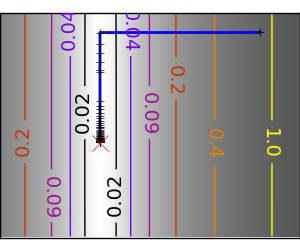
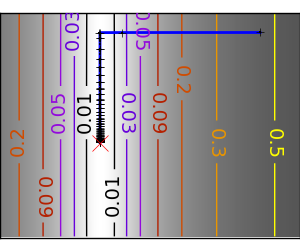
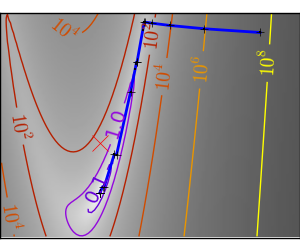
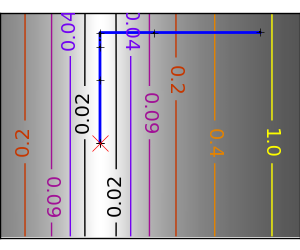
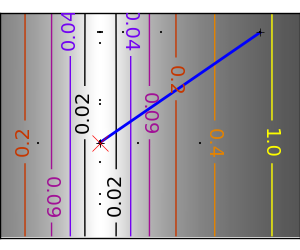
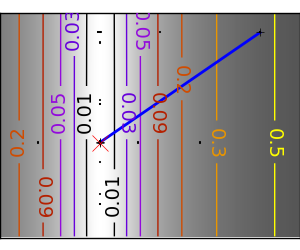
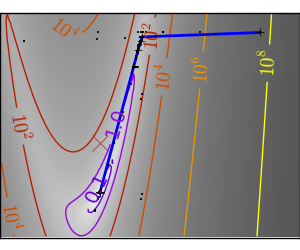
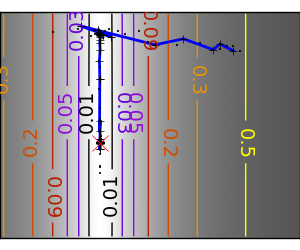
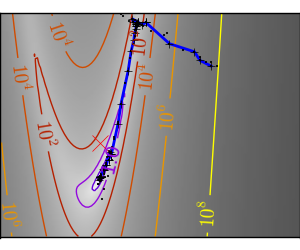
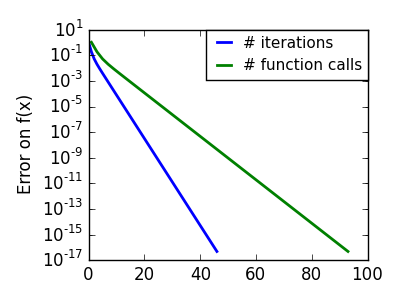
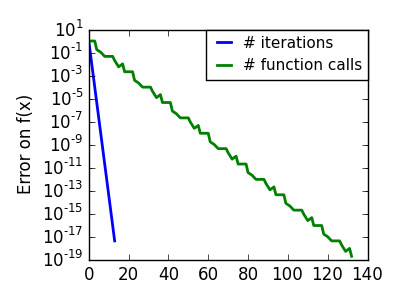
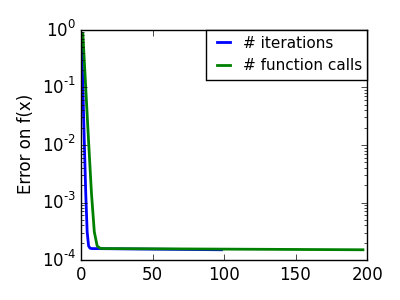
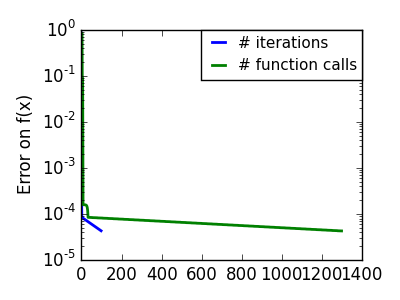
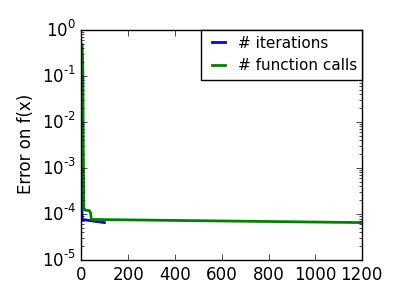
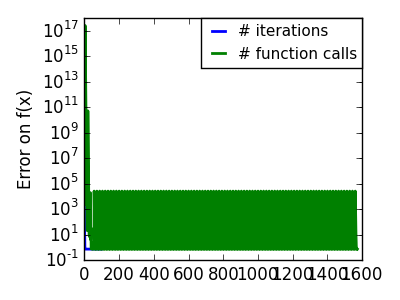
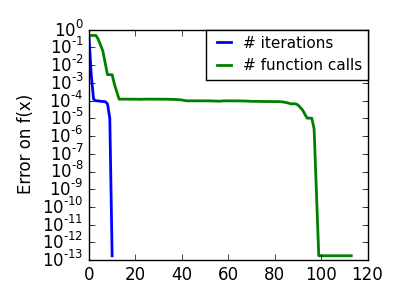
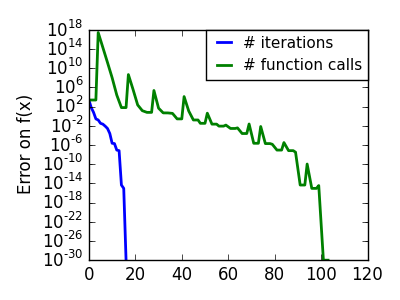
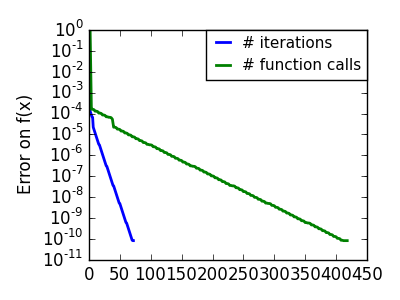
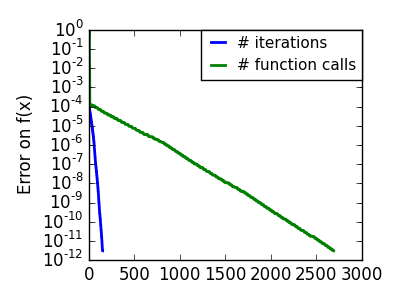
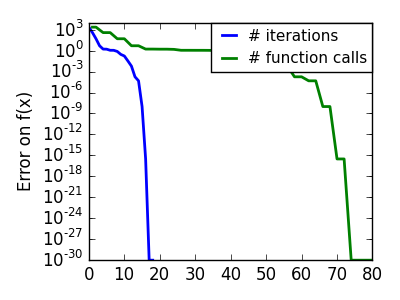
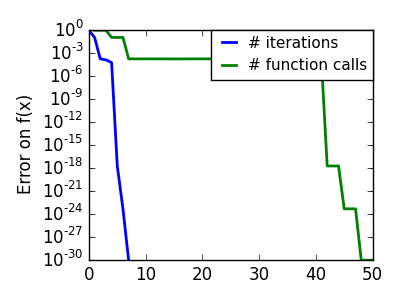
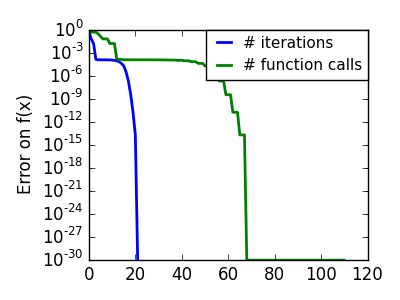
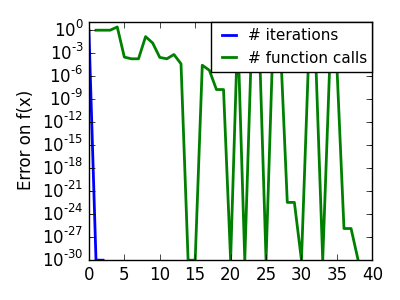
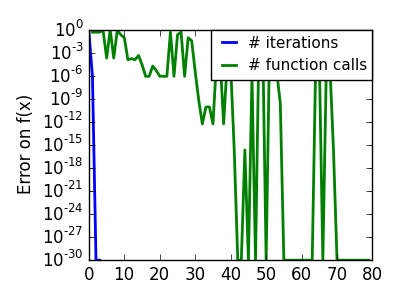
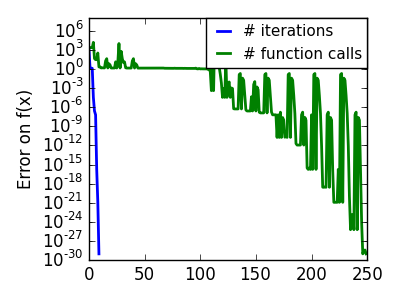
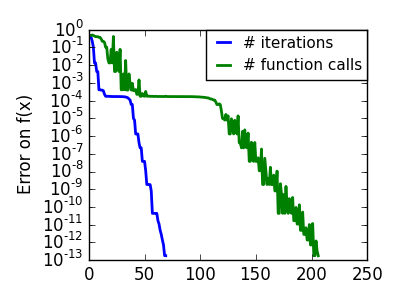
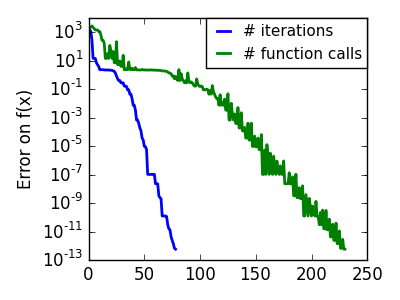
Gradient descent¶
An example demoing gradient descent by creating figures that trace the evolution of the optimizer.
スクリプトの出力:
Warning: Desired error not necessarily achieved due to precision loss.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 10
Function evaluations: 57
Gradient evaluations: 45
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 16
Function evaluations: 43
Gradient evaluations: 43
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 72
Function evaluations: 137
Gradient evaluations: 208
Hessian evaluations: 72
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 151
Function evaluations: 1194
Gradient evaluations: 1344
Hessian evaluations: 151
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 18
Function evaluations: 22
Gradient evaluations: 39
Hessian evaluations: 18
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 7
Function evaluations: 21
Gradient evaluations: 21
Warning: Desired error not necessarily achieved due to precision loss.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 21
Function evaluations: 50
Gradient evaluations: 38
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 19
Function evaluations: 33
Gradient evaluations: 33
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 2
Function evaluations: 35
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 3
Function evaluations: 75
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 9
Function evaluations: 239
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 70
Function evaluations: 136
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.000000
Iterations: 79
Function evaluations: 151
Python ソースコード: plot_gradient_descent.py
import numpy as np
import pylab as pl
from scipy import optimize
from cost_functions import mk_quad, mk_gauss, rosenbrock,\
rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian, LoggingFunction,\
CountingFunction
x_min, x_max = -1, 2
y_min, y_max = 2.25/3*x_min - .2, 2.25/3*x_max - .2
###############################################################################
# A formatter to print values on contours
def super_fmt(value):
if value > 1:
if np.abs(int(value) - value) < .1:
out = '$10^{%.1i}$' % value
else:
out = '$10^{%.1f}$' % value
else:
value = np.exp(value - .01)
if value > .1:
out = '%1.1f' % value
elif value > .01:
out = '%.2f' % value
else:
out = '%.2e' % value
return out
###############################################################################
# A gradient descent algorithm
# do not use: its a toy, use scipy's optimize.fmin_cg
def gradient_descent(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None, adaptative=False):
x_i, y_i = x0
all_x_i = list()
all_y_i = list()
all_f_i = list()
for i in range(1, 100):
all_x_i.append(x_i)
all_y_i.append(y_i)
all_f_i.append(f([x_i, y_i]))
dx_i, dy_i = f_prime(np.asarray([x_i, y_i]))
if adaptative:
# Compute a step size using a line_search to satisfy the Wolf
# conditions
step = optimize.line_search(f, f_prime,
np.r_[x_i, y_i], -np.r_[dx_i, dy_i],
np.r_[dx_i, dy_i], c2=.05)
step = step[0]
if step is None:
step = 0
else:
step = 1
x_i += - step*dx_i
y_i += - step*dy_i
if np.abs(all_f_i[-1]) < 1e-16:
break
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def gradient_descent_adaptative(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
return gradient_descent(x0, f, f_prime, adaptative=True)
def conjugate_gradient(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.fmin_cg(f, x0, f_prime, callback=store, gtol=1e-12)
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def newton_cg(x0, f, f_prime, hessian):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.fmin_ncg(f, x0, f_prime, fhess=hessian, callback=store,
avextol=1e-12)
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def bfgs(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.fmin_bfgs(f, x0, f_prime, callback=store, gtol=1e-12)
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def powell(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.fmin_powell(f, x0, callback=store, ftol=1e-12)
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
def nelder_mead(x0, f, f_prime, hessian=None):
all_x_i = [x0[0]]
all_y_i = [x0[1]]
all_f_i = [f(x0)]
def store(X):
x, y = X
all_x_i.append(x)
all_y_i.append(y)
all_f_i.append(f(X))
optimize.fmin(f, x0, callback=store, ftol=1e-12)
return all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i
###############################################################################
# Run different optimizers on these problems
levels = dict()
for index, ((f, f_prime, hessian), optimizer) in enumerate((
(mk_quad(.7), gradient_descent),
(mk_quad(.7), gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_quad(.02), gradient_descent),
(mk_quad(.02), gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_gauss(.02), gradient_descent_adaptative),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
gradient_descent_adaptative),
(mk_gauss(.02), conjugate_gradient),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
conjugate_gradient),
(mk_quad(.02), newton_cg),
(mk_gauss(.02), newton_cg),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
newton_cg),
(mk_quad(.02), bfgs),
(mk_gauss(.02), bfgs),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
bfgs),
(mk_quad(.02), powell),
(mk_gauss(.02), powell),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
powell),
(mk_gauss(.02), nelder_mead),
((rosenbrock, rosenbrock_prime, rosenbrock_hessian),
nelder_mead),
)):
# Compute a gradient-descent
x_i, y_i = 1.6, 1.1
counting_f_prime = CountingFunction(f_prime)
counting_hessian = CountingFunction(hessian)
logging_f = LoggingFunction(f, counter=counting_f_prime.counter)
all_x_i, all_y_i, all_f_i = optimizer(np.array([x_i, y_i]),
logging_f, counting_f_prime,
hessian=counting_hessian)
# Plot the contour plot
if not max(all_y_i) < y_max:
x_min *= 1.2
x_max *= 1.2
y_min *= 1.2
y_max *= 1.2
x, y = np.mgrid[x_min:x_max:100j, y_min:y_max:100j]
x = x.T
y = y.T
pl.figure(index, figsize=(3, 2.5))
pl.clf()
pl.axes([0, 0, 1, 1])
X = np.concatenate((x[np.newaxis, ...], y[np.newaxis, ...]), axis=0)
z = np.apply_along_axis(f, 0, X)
log_z = np.log(z + .01)
pl.imshow(log_z,
extent=[x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max],
cmap=pl.cm.gray_r, origin='lower',
vmax=log_z.min() + 1.5*log_z.ptp())
contours = pl.contour(log_z,
levels=levels.get(f, None),
extent=[x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max],
cmap=pl.cm.gnuplot, origin='lower')
levels[f] = contours.levels
pl.clabel(contours, inline=1,
fmt=super_fmt, fontsize=14)
pl.plot(all_x_i, all_y_i, 'b-', linewidth=2)
pl.plot(all_x_i, all_y_i, 'k+')
pl.plot(logging_f.all_x_i, logging_f.all_y_i, 'k.', markersize=2)
pl.plot([0], [0], 'rx', markersize=12)
pl.xticks(())
pl.yticks(())
pl.xlim(x_min, x_max)
pl.ylim(y_min, y_max)
pl.draw()
pl.figure(index + 100, figsize=(4, 3))
pl.clf()
pl.semilogy(np.maximum(np.abs(all_f_i), 1e-30), linewidth=2,
label='# iterations')
pl.ylabel('Error on f(x)')
pl.semilogy(logging_f.counts,
np.maximum(np.abs(logging_f.all_f_i), 1e-30),
linewidth=2, color='g', label='# function calls')
pl.legend(loc='upper right', frameon=True, prop=dict(size=11),
borderaxespad=0, handlelength=1.5, handletextpad=.5)
pl.tight_layout()
pl.draw()
Total running time of the example: 19.37 seconds ( 0 minutes 19.37 seconds)